SEBI says wilful defaulters would also be not allowed to take control of any other listed company.
SEBI says wilful defaulters would also be not allowed to take control of any other listed company.
India’s market regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), on Saturday, tightened the rules for so-called wilful defaulters preventing them from raising funds through public issues. The rules, however, are applicable prospectively which suggests that those who have already been termed wilful defaulters may not come within the ambit of these strictures.
Following a board meeting in Delhi, on Saturday, SEBI said that entities declared as wilful defaulters will not be allowed to raise money through sale of shares, debt securities and non-convertible preference redeemable shares to the public.
“No issuer shall make a public issue of equity securities/debt securities/non-convertible redeemable preference shares, if the issuer company or its promoter or its director is in the list of the wilful defaulters,” said a press release issued by SEBI.
Such entities will not be allowed to take control of another listed entity, SEBI said. These firms will also not be allowed to set up market entities like mutual funds. The rules are applicable prospectively, said the regulator.
At a press conference in New Delhi, UK Sinha, chairman of SEBI said that all rules made by the regulator are prospective in nature.
In January 2015, SEBI issued a draft paper proposing that wilful defaulters would not be allowed to sell shares, debt securities and non-convertible preference redeemable shares to the public. The paper had suggested that wilful defaulters be barred from taking control of another listed entity, but that they be allowed to participate in counter offers to deal with hostile takeover bids. Each of these restrictions would be applicable if the issuer, its promoter, group company or director of the issuer of such securities were in the list of wilful defaulters published by RBI, the stock market regulator had said.
The final regulations announced on Saturday are along the same lines.
Policy makers have toughened their stance against wilful defaulters as they try and improve the asset quality of the banking sector. While defaulters who are hit by external factors such as weakness in economic conditions may deserve some help from the system, policy makers feel that wilful defaulters must not be spared.
RBI has been asking banks to get tough on wilful defaulters and has a tough set of rules in place which say that anyone tagged a wilful defaulter cannot raise fresh funds from the banking system. The banking regulator, however, has been of the view that such defaulters also need to have their access to capital markets restricted. This has now happened with SEBI tightening its rules as well.
While RBI has not disclosed the quantum of loans that fall under the wilful default category, data has emerged from some large public sector banks.
Loans worth Rs.11,700 crore given by State Bank of India have been locked up as non-performing assets as nearly 1,160 defaulters have wilfully decided not to repay, PTI reported on 24 February.
Another state-owned lender, Punjab National Bank (PNB), declared 904 borrowers who owed it a combined Rs.10,869.71 crore as of December-end as wilful defaulters. PNB added 140 companies to the list of wilful defaulters in the December quarter alone.
The most prominent case in this regard is the attempt by banks and investigative agencies to recover dues from UB Group chairman Vijay Mallya, who has been declared a wilful defaulter by lenders like State Bank of India. The country’s largest lender had moved the Bangalore debt recovery tribunal (DRT) seeking an arrest warrant against Mallya. On Friday, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) issued summons to Mallya, asking him to be personally present before it on 18 March. The summons is part of ED’s probe into a money laundering case against the former liquor baron.
Definition of control
Separately, the market regulator clarified what the term ‘control’ means in the context of mergers and acquisitions (M&As) by pegging the shareholding threshold of an acquirer at 25%.
“Considering the international practices and the current regulatory environment in India, the definition of control may be amended such that control is defined as (a) the right or entitlement to exercise at least 25% of voting rights of a company irrespective of whether such holding gives de facto control and/or (b) the right to appoint majority of the non-independent directors of a company,” said SEBI in its press release.
The move is aimed at removing ambiguities that companies currently confront during takeovers. Currently, the definition of ‘control’ under the Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers (SAST) Regulations, 2011—popularly known as the Takeover Code—doesn’t specify a threshold for shareholding.
The current takeover code states that an acquirer is in ‘control’ only if the board of the company that’s being acquired gives the former the right to appoint a majority of the directors, and have the final say on management and policy decisions.
The control of management or policy decisions is through shareholding or management rights or shareholders’ agreement or voting agreements.
SEBI has also cleared a framework for protective rights with an exhaustive list of rights that do not lead to acquisition of control.
“An illustrative list of protective rights which would not amount to acquisition of control may be issued. Grant of such protective rights to an investor may be subject to obtaining the public shareholders’ approval (majority of minority),” SEBI said.
Somasekhar Sundaresan, partner, J Sagar Associates, said “The company that is declared to be a willful defaulter ought to be left out of the severity of SEBI’s measures, and instead those in control of the company alone should have been targeted. A defaulter, whether willful or not, requires restructuring, and imposing prohibitions on the business entity could in fact hurt lenders for whose benefit the policy on willful defaulters has been developed. Expanding the scope to directors would also mean that turning around a company that is accused of being a willful defaulter would become impossible since no one would join the board even after throwing out the old promoters. Detailed provisions on when a borrowing entity ceases to be a willful defaulter would be needed—it cannot be after the board is replaced since, so long as it is a willful defaulter, no one would be able to join the board.”
“The move to allow shareholders to confer the power to exercise veto rights to selected investors without getting into whether they mean “control” is a positive measure. Open offers are for the benefit of public shareholders and they must have the power to waive an open offer. This is a very mature measure of reform. Market players would keenly await what SEBI puts out as a list of veto rights aimed at investor protection will not constitute control,” added Sundaresan.
Source: http://www.livemint.com/Money/LSmk1XiZ26pZnyGj5m4ufP/Sebi-bars-wilful-defaulters-from-markets-posts-at-listed-fi.html
 The amount of foreign exchange reserves that the Reserve Bank of India keeps with overseas banks has more than tripled, signalling that it may be preparing to intervene more effectively in the currency market due to impending volatility because of global factors and the possible exodus of about $30 billion of non-resident Indian deposits.
The amount of foreign exchange reserves that the Reserve Bank of India keeps with overseas banks has more than tripled, signalling that it may be preparing to intervene more effectively in the currency market due to impending volatility because of global factors and the possible exodus of about $30 billion of non-resident Indian deposits.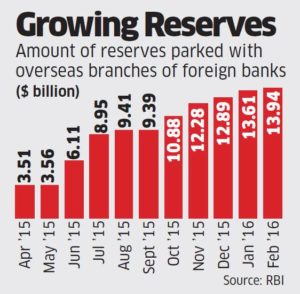 “The rise in deposit component in reserves suggests RBI may be waiting for the right time to invest in overseas assets or parking it in highquality liquid assets for intervention to manage potential currency volatility,” said Vijayan Subramani, managing director, DBS Bank. “Our central bank looks for offshore (sovereign) investment at the right level with a prudent mix of diversification, be it US Treasury or European sovereign bonds.”
“The rise in deposit component in reserves suggests RBI may be waiting for the right time to invest in overseas assets or parking it in highquality liquid assets for intervention to manage potential currency volatility,” said Vijayan Subramani, managing director, DBS Bank. “Our central bank looks for offshore (sovereign) investment at the right level with a prudent mix of diversification, be it US Treasury or European sovereign bonds.”