
India embraced the goods and services tax (GST) on the intervening night of Friday-Saturday, in a move that marked the culmination of the country’s long and chequered journey toward a uniform, all-encompassing, pan-India indirect tax system. The GST would militate against and cut out the cascade of multiple taxes which jack up product prices. The official launch of the tax preceded a grand ceremony in the central hall of Parliament attended by the president and prime minister, along with members of both Houses and the GST Council. Some Opposition parties including the Congress, Trinamool Congress and Left did not attend the ceremony, citing protests against GST by small and medium-scale entrepreneurs, traders, weavers and informal-sector workers.
Although the design of the new destination-based tax on consumption with its multiple rates, sub-optimal coverage and complicated rules is unmistakably inferior to an “ideal GST”, even independent tax experts welcomed the launch, calling it a transformational move. However, trenchant critics would say the imperfect GST has merely enabled cross-utilisation of credit between the central and state VAT chains and is, therefore, akin to the 2004 Cenvat rules that allowed such cross-credit facility between central excise and service tax.
But these critics might have taken too dim a view; GST is a momentous event for thee reasons: One, it puts in place a federal, rules-bound indirect tax system that would curtail the scope of rate differentials for the same products among states (one-product-one-tax) ; two, it could potentially slash India’s high logistics costs by speeding up movement of goods across state borders and even within states and thereby make the country’s goods and services more competitive; and three, thanks to the availability of seamless input tax credits, GST would discourage tax evasion and expand the revenue base for the government without hurting the businesses or the consumers. The GST will subsume excise duty and state VAT (along with the corresponding taxes on imports), service tax, octroi, entry tax, purchase tax, central sales tax, and entertainment tax, but not the basic Customs duty which is the tariff on imports.
 Earlier, the GST Council, which met for an hour, decided to reduce the tax rate on fertilisers from 12% proposed earlier to 5%, a move that would nullify the chances of prices of these key farm inputs rising under GST. The gap between the current tax incidence on fertilisers and the 12% rate had created a practical difficulty in recovering the differential from fertiliser stocks lying with manufacturers and dealers as MRPs are printed on them. Also, the ministry of finance tweeted, the rate for “exclusive parts of tractors” have been reduced to 18% from 28%.
Earlier, the GST Council, which met for an hour, decided to reduce the tax rate on fertilisers from 12% proposed earlier to 5%, a move that would nullify the chances of prices of these key farm inputs rising under GST. The gap between the current tax incidence on fertilisers and the 12% rate had created a practical difficulty in recovering the differential from fertiliser stocks lying with manufacturers and dealers as MRPs are printed on them. Also, the ministry of finance tweeted, the rate for “exclusive parts of tractors” have been reduced to 18% from 28%.
NITI Aayog member Bibek Debroy on Friday rebutted the claim that GST would produce 1.5% increase in GDP. “For an imperfect GST, I have no idea what is the figure. This particular figure (1.5%) was for ideal GST,” he said. Chief economic adviser Arvind Subramanian had told FE earlier that even though “we have not got as much base expansion and as much reduction in complexities as we would have liked”, there was still a huge reduction in complexities. “I expect a 10% expansion in the (tax) base due to just invoice-matching,” he had said.
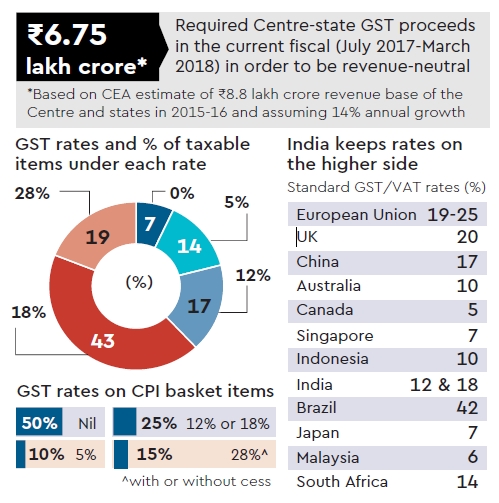
While the government has iterated that the GST would not stoke inflation — GST will be zero on 50% of consumer price index basket and 5% on another 10% — former finance minister P Chidambaram said that the new tax could be inflationary in the short run. However, Subramanian said that with with actual tax incidence to be substantially lower under GST due to input tax credit, a downward bias on prices was to be expected. Firms disposing of stocks could also have a dampening effect on prices in the short run, he added.
Even as the industry is keeping its fingers crossed, the government has assured them that the anti-profiteering provision built into the relevant GST laws to prevent companies from not passing on the tax benefit under GST to consumers would be sparingly used. “I sincerely hope that we don’t have to really use the anti-profiteering mechanism,” Jaitley had said on Thursday. Chidambaram, however, sharply criticised the mechanism, saying it was wrong to assume that “the element of taxes decide at what price I sell my goods”. Since tax is only one of the things that make up costs, he said, if tax falls, it does not mean there should be a corresponding reduction in prices.
Even though 68 lakh businesses have already been issued provisional IDs by GSTN, the IT backbone for the new system, and the deadline for first filing of returns have been postponed to August 20 — invoice-wise returns can be filed as late as the first week of September — concern over the transition pains remained. Arun Kumar, chairman and CEO at KPMG in India, said: “The focus should now be on making the transition seamless and effective. Making compliance cost-effective, particularly for smaller businesses, is extremely important. The potential benefits of this landmark-reform will become real when the benefits of rationalised taxation accrue to consumers and business benefits from cost-efficiencies in logistics and streamlined processes.”
According to Shyamal Mukherjee, chairman, PwC India, “We are confident (that GST) will boost investors’ confidence in India, incentivise manufacturing and fuel the growth of the economy.” When asked about the quantum of extra growth due to GST by a TV channel earlier in the day, the chief economic adviser, however, merely said GST’s effect on the economy would be “positive”. “The medium-term impact of GST on macroeconomic indicators is expected to be extremely positive. Inflation will be reduced as cascading of taxes will be eliminated,” CII director general Chandrajit Banerjee said, adding that exports would emerge as more competitive in global markets, while FDI was likely to be encouraged.





