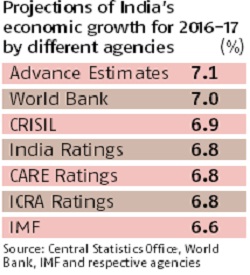
India’s economy could grow at 6.5-6.75% in the current financial year and might not gather significant momentum next year but that doesn’t warrant a fiscal/monetary easing, according to Economic Survey 2016-17 tabled in Parliament on Monday. Projecting a 0.25-0.5% demonetisation-induced reduction in the FY17 gross domestic product (GDP) growth relative to the 7% annual expansion the country would have otherwise reported, the survey cautiously estimated FY18 growth within a broad low-equilibrium range of 6.75-7.5%.
India’s economy could grow at 6.5-6.75% in the current financial year and might not gather significant momentum next year but that doesn’t warrant a fiscal/monetary easing, according to Economic Survey 2016-17 tabled in Parliament on Monday. Projecting a 0.25-0.5% demonetisation-induced reduction in the FY17 gross domestic product (GDP) growth relative to the 7% annual expansion the country would have otherwise reported, the survey cautiously estimated FY18 growth within a broad low-equilibrium range of 6.75-7.5%.
A clutch of states in India have suffered from an “aid curse” — that is, a negative effect on redistributive resource transfers on fiscal effort and governance quality — the survey noted and invited a debate on universal basic income (UBI) for households in these states.
Direct UBI transfers to the households could be a more efficient way to reduce poverty, cementing the recent gains in redistributive efficiency through the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar and mobile) platform, the authors of the survey felt, but they cautioned against UBI implementation until the tax-GDP ratio showed tangible rise.
“There is a big potential to improve the weak targeting of current (anti-poverty) schemes,” chief economic adviser Arvind Subramanian said, amid rumours that Wednesday’s Union Budget might launch a pilot UBI.
According to the survey, the short-term effect of the note ban on the economy will be less adverse than many others predicted: The International Monetary Fund (IMF), for instance, saw a 1 percentage point growth reduction in FY17; the Reserve Bank of India had pegged a 0.5% loss in growth. The IMF, Subramanian said, relied on an “over-optimistic baseline”.
Given that growth was 7.2% in the first half of this fiscal and the survey assumption is against the baseline scenario of around 7% FY17 growth, the forecast is that second-half growth, at worst, could be around 6%.
This is still a bit more optimistic than what many independent analysts prognosticated — Morgan Stanley Research, for instance, put H2 FY17 growth at 5.5%.
However, the survey appreciated the limitation of capturing informal activity in the national income data, suggesting the pain of note recall might have been more severe. A set of structural reforms could take the economy towards the potential real GDP growth of 8-10%.
As for FY18, exports, which are “recovering”, based on an uptick in the global economy — the IMF has projected global growth to rise to 3.4% in 2017 from 3.1% in 2016 — would be a significant growth driver, the survey said, but admitted that the outlook for private consumption was less clear (oil prices are a potential drag while low interest rates might help a smart recovery in spending on housing and consumer durables). It also said candidly that given the sticky TBS or twin balance sheet problem, private investment was unlikely to recover from the FY17 level (fixed investment, according to the central statistics office, declined 0.2% this fiscal and investment as a share of GDP is now seen at 29%, down 5 percentage points from FY12). Demand-driven remonetisation, a push to digital payments using incentives, bringing land and real estate into the goods and services tax (GST) net, lowering tax rates and stamp duties and improving the tax system would help take growth back to trend in FY18, it said. However, the threat of trade tensions among major countries prevailed, especially given the Trump administration’s proclivity to step into a protectionist groove.
Giving the fiscal outlook for the Centre, the survey warned that the increase in tax-GDP ratio of about 0.5 percentage point each in the last two years owing to the oil windfall would disappear in FY18: “Excise-related taxes will decline by about 0.1 percentage point of GDP, a swing of about 0.6 percentage points relative to FY17,” it said. According to Crisil Research, about a third of the likely excise revenue of Rs 2.3 lakh crore in FY17 could be ascribed to excise duty increases on petroleum products. There would be windfalls from cessation of the RBI’s liability with respect to demonetised banknotes not returned to banks and the new income disclosure scheme PMGKY. Revenue potential from GST could, however, take some some time to be fully exploited.
While a committee on fiscal consolidation is believed to have recommended some well-defined escape clauses to provide the fiscal support to consumption and investment in the near term, the survey noted that primary balance (obtained after netting interest payments from the fiscal deficit) needed more attention. “The vulnerability is the country’s primary deficit… Put simply, India’s government is not collecting enough revenue to cover its running costs, let alone the interest on its debt obligations.” Although the survey noted that there was nothing extraordinary about this (other emerging market economies too run primary deficits), given India’s rapid rates of growth, its primary deficit should have been much lower than others.
This is still a bit more optimistic than what many independent analysts prognosticated — Morgan Stanley Research, for instance, put H2 FY17 growth at 5.5%.
However, the survey appreciated the limitation of capturing informal activity in the national income data, suggesting the pain of note recall might have been more severe. A set of structural reforms could take the economy towards the potential real GDP growth of 8-10%.
As for FY18, exports, which are “recovering”, based on an uptick in the global economy — the IMF has projected global growth to rise to 3.4% in 2017 from 3.1% in 2016 — would be a significant growth driver, the survey said, but admitted that the outlook for private consumption was less clear (oil prices are a potential drag while low interest rates might help a smart recovery in spending on housing and consumer durables). It also said candidly that given the sticky TBS or twin balance sheet problem, private investment was unlikely to recover from the FY17 level (fixed investment, according to the central statistics office, declined 0.2% this fiscal and investment as a share of GDP is now seen at 29%, down 5 percentage points from FY12). Demand-driven remonetisation, a push to digital payments using incentives, bringing land and real estate into the goods and services tax (GST) net, lowering tax rates and stamp duties and improving the tax system would help take growth back to trend in FY18, it said. However, the threat of trade tensions among major countries prevailed, especially given the Trump administration’s proclivity to step into a protectionist groove.
Giving the fiscal outlook for the Centre, the survey warned that the increase in tax-GDP ratio of about 0.5 percentage point each in the last two years owing to the oil windfall would disappear in FY18: “Excise-related taxes will decline by about 0.1 percentage point of GDP, a swing of about 0.6 percentage points relative to FY17,” it said. According to Crisil Research, about a third of the likely excise revenue of Rs 2.3 lakh crore in FY17 could be ascribed to excise duty increases on petroleum products. There would be windfalls from cessation of the RBI’s liability with respect to demonetised banknotes not returned to banks and the new income disclosure scheme PMGKY. Revenue potential from GST could, however, take some some time to be fully exploited.
While a committee on fiscal consolidation is believed to have recommended some well-defined escape clauses to provide the fiscal support to consumption and investment in the near term, the survey noted that primary balance (obtained after netting interest payments from the fiscal deficit) needed more attention. “The vulnerability is the country’s primary deficit… Put simply, India’s government is not collecting enough revenue to cover its running costs, let alone the interest on its debt obligations.” Although the survey noted that there was nothing extraordinary about this (other emerging market economies too run primary deficits), given India’s rapid rates of growth, its primary deficit should have been much lower than others.
Source: http://www.financialexpress.com/budget/economic-survey-2017/union-budget-2017-economic-survey-says-reforms-to-power-india-potential-growth/531664/



 It led the Centre to airlift national gold reserves as a pledge to the IMF in exchange for a loan to cover balance of payment debts.
It led the Centre to airlift national gold reserves as a pledge to the IMF in exchange for a loan to cover balance of payment debts.