
Increasing the fear of an unravelling of the exercise of invoices-matching, which is crucial to realising the presumed merits of the goods and services tax (GST), like reduction of tax evasion and cascades, three-fourths of the 60 lakh eligible taxpayers haven’t completed the formalities of filing both the inward and outward supplies-based returns for July till a day before the October 31 deadline. This has forced the government to give another window till November-end “to facilitate about 30.81 lakh taxpayers” to file details of inward supplies (GSTR-2). The triplicate comprehensive returns for July, the first month since GST’s launch, were originally required to be filed in the subsequent month itself, but due to the GST Network’s technical glitches and low levels of compliance, the deadlines have been extended multiple times. The schedule for filing these returns for August onwards has not even been announced yet, as this was to follow from the July-cycle learning. While invoice-matching is getting unduly delayed, piling up a huge job for the taxmen, the consequent blockage of input tax credits is bound to hit the working capital for large sections of the industry.
Since the launch of GST, small and medium enterprises have faced cash crunch, while exporters have got the refunds of July and August taxes only recently. Of course, the government has allowed industries with turnover up to Rs 1.5 crore to file the detailed returns on a quarterly basis while assuring them of prompt release of input tax credits claimed via monthly interim returns, but the deferment of invoices-matching would mean large-scale adjustments of the tax and ITC figures later. The government has faced much criticism for the imperfections of the GST it launched (multiple rates, high peak rates, exclusion of real estate and five petro- leum products etc). Also, since the GST was introduced, it has had to make more compromises that besmirched the new tax further. While dozens of items saw rate changes post-July, the GST Council, on October 6, accorded virtual tax waiver for exporters till March 31, 2018, despite exemptions running contrary to the GST’s basic tenet.
Besides, units with up to Rs 1.5 crore turnover were allowed to file quarterly instead of monthly returns, a move that would allow 90% of the non-composition GST registrants to shift to the easier system of filing returns every quarter, but could make prompt invoices-matching difficult. As reported by FE on Monday, the council may allow all taxpayers to move to quarterly mode of filing returns as it meets at Guwahati on November 10. The composition scheme — that allows businesses to pay taxes as a small percentage of turnover annually — is set to be made available to units with turnover up to Rs 1.5 crore, in what could effectively exclude 90% of the taxpayers from being part of the multi-point destination-based tax chain.
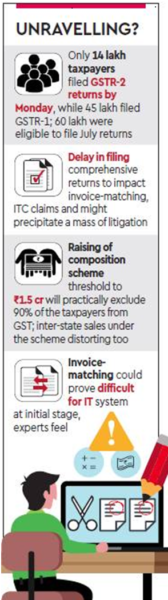 GST Network, which is the IT backbone of GST, estimates that about 80 crore invoices would be uploaded on to the system every month. A tax official said that even if 2-3 crore of the invoices don’t match, it will lead to numerous disputes, which would be arduous to resolve. “Besides, tax evasion takes place when transactions are off-book which will never be captured through invoices. The government needs precise and visible enforcement to minimise tax evasion,” the official said. To begin with, GST Council should have implemented matching at the GST level where sale and purchase are matched on the basis of the unique GST registration number of each taxpayer. Invoice matching should ideally have been brought in a few months later after the system stabilised. Now that some taxpayers are allowed to file returns only quarterly, the matching should also be harmonised with it and not be carried out every month.
GST Network, which is the IT backbone of GST, estimates that about 80 crore invoices would be uploaded on to the system every month. A tax official said that even if 2-3 crore of the invoices don’t match, it will lead to numerous disputes, which would be arduous to resolve. “Besides, tax evasion takes place when transactions are off-book which will never be captured through invoices. The government needs precise and visible enforcement to minimise tax evasion,” the official said. To begin with, GST Council should have implemented matching at the GST level where sale and purchase are matched on the basis of the unique GST registration number of each taxpayer. Invoice matching should ideally have been brought in a few months later after the system stabilised. Now that some taxpayers are allowed to file returns only quarterly, the matching should also be harmonised with it and not be carried out every month.
These steps alone will make the process smoother,” Rahul Renavikar, managing director of Acuris Advisors said. Aditya Singhania, of Taxmann, said: “The matching concept is a much appreciated step for allowing input tax credit which is regulated by the GSTR 1, 2 and 3 mechanism. But with the brilliant concept, the IT platform of GST i.e. www.gst.gov.in should equally work in same wavelength for achieving the objective. Due to certain bugs and frictions, coupled with totally new forms of returns, taxpayers were unable to file the (returns) on time.” While industrialised states like Maharashtra, Gujarat and Karnataka among others had invoice-matching systems prior to GST, although these were not granular-level matching. A Maharashtra tax official, who requested anonymity, said that matching at the level of VAT number –much simpler than invoice-level matching – had enabled identification of 80% mismatches, which enabled the tax department to take action against hawala operations.
However, some tax officials have doubted the efficacy of invoice-matching, saying this wasn’t much of a success in any country with GST-type tax. “The first two month would pose immense challenges on how to deal with invoice mismatches and the provision may eventually have to be done away with,” a revenue department officials told FE on the condition of anonymity. The tax department is also worried that about 40% of taxpayers who filed the returns for July have claimed nil-tax liability. “It is indeed a large number. If enforcement is required, we will carry it out, though not in the nature of search and seizure. We may opt for discreet inquiries and meetings with such groups of taxpayers, to find out the reasons for the trend,” revenue secretary Hasmukh Adhia had told FE earlier.





