Seeking to crackdown on shell companies, the government has proposed to remove exemption available to firms with tax liability of up to Rs 3,000 from filing I-T returns beginning next fiscal.
The Union Budget 2018-19 has rationalised the I-T Act provision relating to prosecution for failure to furnish returns.
Thus, a managing director or a director in charge of the company during a particular financial year could be liable for prosecution in case of any lapse in filing I-T returns for any financial year beginning April 1.
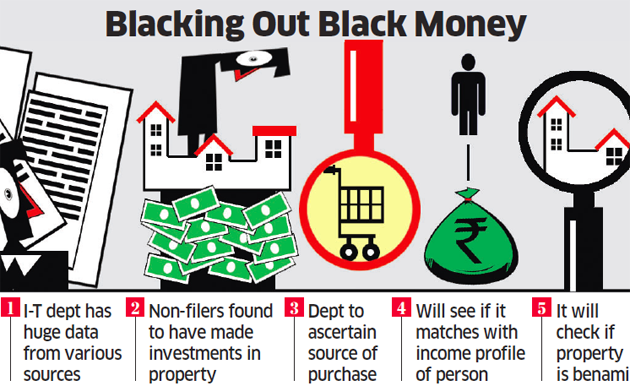
“The income tax departments would now track investments by these companies. Also, the focus will be on those firms that show less profit and also those who file I-T returns for the first time,” a senior finance ministry official said.
There are around 12 lakh active companies in the country, out of which about 7 lakh are filing their returns, including annual audited report, with the ministry of corporate affairs. Of this, about 3 lakh companies show ‘nil’ income.
The Section 276CC of the Income Tax Act provided that if a person wilfully fails to furnish in due time the return of income, he shall be punishable with imprisonment and fine.
However, no prosecution could be initiated if the tax liability of an assessee does not exceed Rs 3,000.
The government has amended the provision with effect from April 1, 2018 and removed the exemption available to companies.
“In order to prevent abuse of the said proviso by shell companies or by companies holding benami properties, it is proposed to amend the provisions… so as to provide that the said sub-clause shall not apply in respect of a company,” it said.
The official said that as many as 5 lakh are companies not filing returns and they could be a potential source of money laundering. “These could be small firms which are engaged in honest business, but there could be some which are a potential threat. We have to look into the data.”
Nangia & Co Managing Partner Rakesh Nangia said though the amendment has been brought about to prevent abuse by shell companies/benami properties, checks similar to those placed in the law for invoking GAAR, should be in place to avoid genuine hardship.
“Though the taxman may be driven by compulsions to ensure proper tax compliance, care must be taken while taking such action. In most developing countries, prosecution for tax matters is applied only in cases of serious tax frauds and not in general compliance matters,” Nangia said.
The Budget announcement follows the recommendation of the task force on shell companies, which was set up in February last year.
In the government’s fight against black money, shell companies have come to the fore as they are seen as potential for money laundering.
Till the end of December 2017, over 2.26 lakh companies were deregistered by the MCA for various non-compliances and being inactive for long.
Shell companies are characterised by nominal paid-up capital, high reserves and surplus on account of receipt of high share premium, investment in unlisted companies, no dividend income and high cash in hand.
Also, private companies as majority shareholders, low turnover and operating income, nominal expenses, nominal statutory payments and stock in trade, minimum fixed asset are some of the other characteristics.
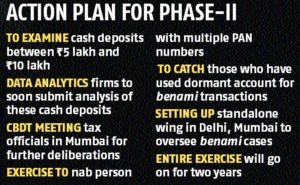
Since last year, the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) — the apex policy making body of the I-T department — has been sharing with the MCA specific information like PAN data of corporates, Income Tax returns (ITRs), audit reports and statement of financial transactions (SFT) received from banks.
Source: Times of India