 Domestic investors have a lot to learn from their foreign institutional counterparts, who seem to have mastered the art of timing, raking in the moolah in the midst of market volatility.
Domestic investors have a lot to learn from their foreign institutional counterparts, who seem to have mastered the art of timing, raking in the moolah in the midst of market volatility.
On the other hand, domestic investors mostly buy when foreign institutional investors (FIIs) are booking profits at higher valuations, limiting their own upside.
For example, in the current rally, most of the FII purchases were in 2012 and the first half of 2013, when the price-to-earnings (PE) multiple of BSE 500 companies had hit a multi-year low.
In contrast, most of the accumulation by domestic investors, through mutual funds and insurance companies, occurred in 2015 when BSE 500 companies were trading at a multi-year PE high. FIIs accumulated India’s top-listed companies at an average valuation of around 16 times and offloaded it to domestic investors at around 24 times their value (see chart).
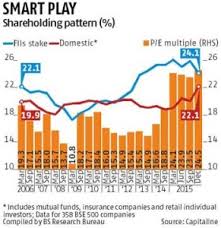
In all, FIIs’ stake in BSE 500 companies was up 550 basis points between March 2012 and March 2015, at an average PE of around 16 times the companies’ combined trailing 12-month net profits. FIIs stake peaked in the March 2015 quarter, coinciding with the peak in valuations of BSE 500 companies. One basis point is one-hundredth of a per cent.
The analysis is based on the end-of-quarter shareholding pattern, market capitalisation and quarterly net profit of BSE 500 companies, beginning the March 2006 quarter. The sample is based on the data for 358 companies where the data is comparable across the period.
Analysts attribute this to the steady nature of fund flows FIIs receive, while domestic institutional investors are at the mercy of inflows from retail investors, which tend to take place late in the cycle.
“When FIIs were buying in 2012-13, insurance companies and mutual funds were still facing redemption, forcing fund managers to sell their holdings even when the valuations were low. Inflows turned positive only in late 2014 and 2015, when domestic retail investors were convinced about the rally,” said Dhananjay Sinha, head, institutional equities, Emkay Global Financial Services.
In comparison, FIIs receive a significant portion of their funds from large institutional investors in Europe and the US, whose investment sentiment remains steady over a long period.
Others also point to differences in the investing styles of FIIs and their domestic counterparts.
“FII investments are largely fundamental and research-driven compared to domestic investors, most of whom tend to get swayed by market sentiment and herd mentality,” said G Chokkalingam, the founder and chief executive officer of Equinomics Research & Advisory.
This explains why a majority of domestic investors fail to make money in the market, he added.
A similar trend was visible in the rally before the global financial crisis, when FIIs were net sellers for nearly two years in the run-up to the September 2008 crash while domestic investors were buyers.
Despite the trends, some analysts differ.
Nitin Jain, the president and chief executive officer of global asset and wealth management firm Edelweiss Capital, said there is no evidence of domestic investors being less smart than their foreign counterparts.
“We should not paint all FIIs with the same brush. Investment flows from exchange-traded funds, which is retail money – as volatile and sentiment-driven as domestic retail and mutual funds flows. FIIs, on the other end of the spectrum, also get pension money and sovereign wealth funds, which are long-term and their investment style is similar to that of domestic insurance companies,” said Jain.





