 A multi-agency clampdown has begun on shell companies to tackle the black money menace wherein the role of auditors has come under the scanner for alleged connivance in facilitating illegal transactions.
A multi-agency clampdown has begun on shell companies to tackle the black money menace wherein the role of auditors has come under the scanner for alleged connivance in facilitating illegal transactions.
The auditors’ role is also being looked into for not raising the red flag as several cases have come to the fore, including at listed companies, for alleged mismatch in financial statements, sharp erosion in net worth, siphoning off funds to group and promoter entities, sources said.
Stepping up the vigil, the corporate affairs ministry as well as Sebi and other regulatory authorities are keeping a close tab on activities carried out by shell companies.
Sources said regulatory agencies are examining the role of auditors to ascertain whether they were also involved in suspected illegal activities.
The ministry as well as Sebi are closely looking at the functioning of auditors in various companies, especially those that have not been carrying out business for long. After a detailed analysis, the authorities would decide on the next course of action, sources added.
Auditors, who have greater responsibilities under the Companies Act, 2013, are required to ensure that financial statements of a company are proper and can red flag dubious transactions.
As part of larger efforts to fight illicit fund flows and tax evasion, the ministry has already struck off the names of over two lakh companies from the records and further action is expected.
Besides, Sebi has taken against 331 listed entities that are suspected shell companies. While the watchdog had imposed strict trading restrictions on these scrips, curbs have been eased in some cases after the companies went on appeal against Sebi’s move.
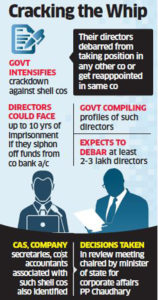
On Tuesday, the government said more than 1.06 lakh directors would be disqualified for their association with shell companies.
The ministry, which is implementing the companies law, has also identified professionals, chartered accountants, company secretaries and cost accountants associated with the defaulting companies.
Besides, such people “involved in illegal activities have been identified in certain cases and the action by professional institutes such as ICAI, ICSI and ICoAI is also being monitored”, an official release said on Tuesday.
Separately, authorities are looking at the possibility of having stricter scrutiny of global auditing firms to make them more accountable with such auditors coming under the lens in various corporate misdoings.
A big area of concern pertains to the big guns seeking to wash off their hands whenever their names crop up in any accounting wrong-doing while their delaying tactics in the name of jurisdiction have also been noticed, an official had said earlier.
While discussions on having tighter regulations for foreign audit firms are going on, the ministry is already examining the recommendations of the 3-member expert panel on various issues related to audit firms amid concerns over certain practices circumventing regulations.






 The government has shared sector-wise “risk factors” companies might exploit to avoid paying GST. According to the tax official quoted above, categorisation or risk evaluation for these audits has been created by using Big Data analytics.
The government has shared sector-wise “risk factors” companies might exploit to avoid paying GST. According to the tax official quoted above, categorisation or risk evaluation for these audits has been created by using Big Data analytics.