India has been ranked as the 40th most competitive economy — slipping one place from last year’s ranking — on the World Economic Forum’s global competitiveness index, which is topped by Switzerland.
On the list of 137 economies, Switzerland is followed by the US and Singapore in second and third places, respectively.
In the latest Global Competitiveness Report released today, India has slipped from the 39th position to 40th while neighbouring China is ranked at 27th.
“India stabilises this year after its big leap forward of the previous two years,” the report said, adding that the score has improved across most pillars of competitiveness. These include infrastructure (66th rank), higher education and training (75) and technological readiness (107), reflecting recent public investments in these areas, it added.
According to the report, India’s performance also improved in ICT (information and communications technologies) indicators, particularly Internet bandwidth per user, mobile phone and broadband subscriptions, and Internet access in schools.
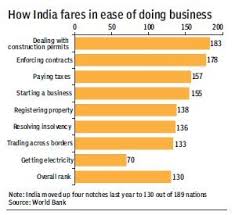
However, the WEF said the private sector still considers corruption to be the most problematic factor for doing business in India.
“A big concern for India is the disconnect between its innovative strength (29) and its technological readiness (up 3 to 107): as long as this gap remains large, India will not be able to fully leverage its technological strengths across the wider economy,” it noted.
Among the BRICS, China and Russia (38) are placed above India.South Africa and Brazil are placed at 61st and 80th spots, respectively.
In South Asia, India has garnered the highest ranking, followed by Bhutan (85th rank), Sri Lanka (85), Nepal (88), Bangladesh (99) and Pakistan (115).
“Improving ICT infrastructure and use remain among the biggest challenges for the region: in the past decade, technological readiness stagnated the most in South Asia,” WEF said.
Other countries in the top 10 are the Netherlands (4th rank), Germany (5), Hong Kong SAR (6), Sweden (7), United Kingdom (8), Japan (9) and Finland (10).
The Global Competitiveness Index (GCI) is prepared on the basis of country-level data covering 12 categories or pillars of competitiveness.
Institutions, infrastructure, macroeconomic environment, health and primary education, higher education and training, goods market efficiency, labour market efficiency, financial market development, technological readiness, market size, business sophistication and innovation are the 12 pillars.
According to WEF’s Executive Opinion Survey 2017, corruption is the most problematic factor for doing business in India.
The second biggest bottleneck is ‘access to financing’, followed by ‘tax rates’, ‘inadequate supply of infrastructure’, ‘poor work ethics in national labour force’ and ‘inadequately educated work force’, among others.
The survey findings are mentioned in the report.
“Countries preparing for the Fourth Industrial Revolution and simultaneously strengthening their political, economic and social systems will be the winners in the competitive race of the future,” WEF founder and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab said.