 India continues to rank low at 130th position in terms of ease of doing business, with the country seeing little or no improvement in dealing with construction permits, getting credit and other parameters.
India continues to rank low at 130th position in terms of ease of doing business, with the country seeing little or no improvement in dealing with construction permits, getting credit and other parameters.
In the World Bank’s latest ‘Doing Business’ report, India’s place remained unchanged from last year’s original ranking of 130 among the 190 economies that were assessed on various parameters. However, the last year’s ranking has been now revised to 131 from which the country has improved its place by one spot.
The government has been making efforts to further improve the ease of doing business and aims to bring the country in the top 50.
Expressing disappointment over no change in India’s ranking in the World Bank’s index on ease of doing business, Indian government regretted that the report did not take into consideration 12 key reforms undertaken by the government.
When it comes to ‘distance to frontier’ — a measurement of the gap between an economy’s performance and the best practice score of 100 — India’s score has improved to 55.27 this year from 53.93 last year.
India is the only country for which the report has a box dedicated to its ongoing economic reforms.
The list of countries in the Doing Business 2017 is topped by New Zealand while Singapore is ranked second. It is followed by Denmark, Hong Kong, South Korea, Norway, the UK, the US, Sweden and former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.
Neighbouring Pakistan is ranked 144th in the list.
On the basis of reforms undertaken, the top 10 improvers are Brunei Darussalam, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Belarus, Indonesia, Serbia, Georgia, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates and Bahrain.
A record 137 economies around the world have adopted key reforms that make it easier to start and operate small and medium-sized businesses, the report said.
Developing countries carried out more than 75 per cent of the 283 reforms in the past year, with Sub-Saharan Africa accounting for over one-quarter of all reforms, it added.
“What we have seen is a remarkable effort on the part of the government to implement business reforms. It looks like we are going to have to wait for another year or so. But the direction of change is fundamentally a very significant one,” Global Indicators Group Director Augusto Lopez-Claros told PTI in an interview.
The rankings are based on ten parameters — starting a business, dealing with construction permits, getting electricity, registering property, getting credit, protecting minority investors, paying taxes, trading across borders, enforcing contracts and resolving insolvency.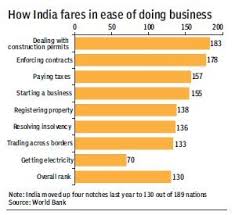
India has improved its ranking with respect to various areas. In terms of getting electricity, the country’s position has jumped to 26th spot from 51st place last year.
When it comes to trading across borders, the ranking has moved up one place to 143, and in enforcing contracts the rise is of six spots to 172nd position.
However, with respect to starting a business, the ranking has slipped four places to 155th spot and in the case of dealing with construction permits by one rank to 185th.
As per the report, India’s ranking in terms of protecting minority investors dropped to 13th place from 10th position last year.
With regard to getting credit, the ranking has fallen by two places to 44.
Explaining as to why India’s reform efforts is not being reflected in the ease of doing business report, Lopez-Claros said it very often takes some time for the reforms implemented by governments about the regulatory environment to be felt on the ground by the business community.
Rita Ramalho, Manager of the Doing Business project said that there were in fact improvements this year.
“There are four areas of improvement this year in India getting electricity, trading across border, enforcing contracts and paying taxes,” Ramalho told PTI.
India’s ranking is based on the study of the system in the two cities of Mumbai and New Delhi.
“The reason why there is no real movement in the ranking is more to do with the fact that other countries are also moving. In absolute terms India, does improve significantly.
There aren’t many countries that improved more than India in terms of absolute number,” Ramalho said.
The ‘Doing Business’ project provides objective measures of business regulations for local firms in economies and selected cities at the sub-national level.
The World Bank is emphasising that countries pay attention to what it calls “distance to frontier” which is an absolute metric, Lopez-Claros said.
“There has been actually substantial increase in the last 12 months in India by couple of percentage points, which is quite large,” he noted.
Source: http://www.businesstoday.in/current/economy-politics/india-ranks-130th-in-ease-of-doing-business-index/story/238944.html







