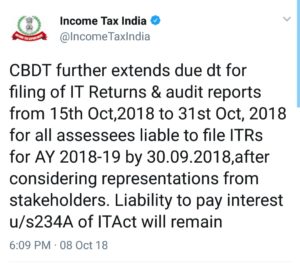
• This move will apply for all those assessees who have business income and file the returns specified for those with this income i.e. ITR 3 to ITR -7.
• Before sharing any information, the income tax authority shall determine that such information is necessary for the GSTN authority to perform its functions.
The government on Tuesday authorized the income tax department to share details including sales and profits that businesses have reported in their income tax returns with GSTN, the company that processes Goods and Services Tax (GST) returns, to scale up scrutiny and check tax evasion.
The move will allow direct and indirect tax authorities to zero in on discrepancies in the information that business have disclosed in their respective tax return forms and nail tax evaders. The move comes as part of tightening of anti-evasion measures after the GST Council gave several relaxations in recent months to ease the rigors of tax compliance to businesses, especially to small ones. A formal system of data sharing between direct and indirect tax authorities means businesses have to be extra careful while filling up their tax returns and avoid mismatches. The move is significant considering that businesses did not show enthusiasm in opting for a single window tax facility for corporate tax, service tax and central excise in 2006 under the name Large Taxpayer Unit as they apparently preferred to avoid simultaneous scrutiny by different tax authorities.
An office order issued by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) on Tuesday authorized the Principal Director General of Income Tax (systems) or Director General of Income Tax (systems) to share specified data with an officer of GSTN. The designated officers from both sides will also decide ways of simultaneous exchange of information
==============================================================================
Order. F. No. 225/105/2019/ITA.ll Order Under Section 138(1)(a) of the Income Tax Act, 1961
F. No. 225/105/2019/ITA.ll
Government of India
Ministry of Finance
Department of Revenue
Central Board of Direct Taxes
New Delhi, the 30th April, 2019
Order In exercise of powers conferred under section 138(1)(a) of the Income tax Act, 1961 (‘Act’), for purposes of sub-clause (i) of section 138(1)(a) of the Act, the Central Board of Direct taxes (‘CBDT’) hereby directs that Principal Director General of Income-tax (Systems) or Director General of Income-tax (Systems), New Delhi shall be the specified income-tax authority for furnishing information respecting assessees to the Nodal Officer, Goods and Services Tax Network (‘GSTN’).
2. The data/information to be furnished by the specified income-tax authority shall be: (a) Request based exchange of data, wherein, important financial fields which are captured in the Income Tax Returns (ITRs) such as (i) status of filing of ITR; (ii) turnover; (iii) gross total income, (iv)turnover ratio; (v) GTI range; (vi) turnover range and (vii) any other field, the modalities of which shall be decided by the concerned specified authorities. (b) Spontaneous exchange of data, the modalities of which shall be decided by the concerned specified authorities. (c) Automatic exchange of data, the modalities of which shall be decided by the concerned specified authorities.