IMF has underscored the significance of reforms in other key sectors like education, health and improving the efficiency of the banking and financial systems.
The Indian economy now seems to be on its way to recovering from disruptions caused by demonetisation and roll-out of goods and services tax, the IMF said today. At the same time, the IMF has underscored the significance of reforms in other key sectors like education, health and improving the efficiency of the banking and financial systems.
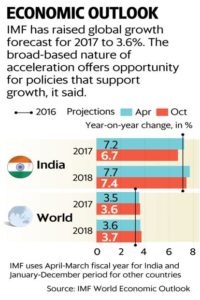
India’s economy has expanded strongly in recent years, thanks to macroeconomic policies that emphasise stability and efforts to tackle supply-side bottlenecks and structural reforms. Disruptions from demonetisation and the rollout of the goods and services tax (GST) did slow growth,” Tao Zhang, Deputy Managing Director of IMF, told PTI in an interview.
“However, with the economy expanding by 7.2 per cent in the latest quarter, India has regained the title of the fastest-growing major economy, Zhang said.
Calling this development a “welcome change”, Zhang said the growth prospects remain positive.
“That said, the Indian economy would benefit from further reforms, such as enhancing health and education, encouraging private and public investment, and improving the efficiency of the banking and financial system. This would support durable and inclusive growth and enable India to move toward the income levels of wealthier countries, the top IMF official said ahead of his visit to India.
Yet the complexities and glitches in GST implementation also resulted in short-term disruptions. As I mentioned earlier, the economy now seems to be on its way to recovering from those disruptions, Zhang said in response to a question.
When asked about the latest Indian budget, which many critics say is protectionist in nature, Zhang said IMF research indicates that tariffs are broadly contractionary, reducing output, investment, and employment.
Trade tariffs may give limited relief to industries and workers that directly compete with affected imports. However, they can raise costs to consumers and other businesses that use the protected products. Tariffs also would reduce incentives for businesses to compete and improve efficiency, he cautioned.
Since the opening of the economy starting in the early-1990s, India has benefitted from trade liberalization, he observed.
Further supply-side reforms aimed at improving the business climate could enhance these benefits, the top IMF official asserted.
Noting that the IMF and India have close relations, and the two have always been good partners, Zhang said his visit is a reflection of this partnership, as is the newest regional capacity development center, SARTTAC, based in New Delhi.
The center partners with India and its South Asian neighbors to build strong institutions and implement policies that promote growth and poverty reduction in the region, he said.
My visit is an opportunity to exchange views with the Indian authorities, senior RBI officials, and representatives from the Indian business community, civil society, and others, he said.
Zhang will also have a presentation on financial technology that will take place on Monday at the National Stock Exchange of India.
We will go over the latest trends in financial technology and their effects on the global economy and India, said the top IMF official.
Source: NDTV