The financial statements and annual returns of all company must be filed on time with the ROC / MCA each year. As per Companies Act, 2013, non-filing of annual return is an offence, consequences of which affect the directors, as well as the company.
Hence, it is a must for every company to file with the MCA:
1. The annual return within 60 days of the Annual General Meeting and
2. The Financial Statement, within 30 days of the Annual General Meeting.
The various consequences and the penalties for not filing annual return of a company (Forms MGT-7 & AOC-4) are highlighted here.
A. Consequences – for Directors
The Directors of a company are responsible for ensuring the compliance of the company with all applicable rules and regulations. When a company defaults on compliance or dues payable, the Directors are held responsible for the default. The following are penal consequences for a Director of a company for default of non-filing of the Annual Return.
Director Disqualification
In case a company has not been filed its Annual Return for three continuous financial years, then every person who has been a director or is currently the director of the specific company could be disqualified under the Companies Act, 2013. If a Director is disqualified, his/her DIN would become inactive and the person would not be eligible to be appointed as a Director of any company for a period of five years from the date of disqualification. Further, disqualified Directors would not also be allowed to incorporate another company for a period of five years.
Fine & Imprisonment
A director of the company can be punished if the company has not been filed even after 270 days from the date when the company should have originally filed with additional penalty. Any Director who has defaulted in the filing of annual return of a company can also be penalized with an imprisonment of a term extended up to six months or with a fine of an amount not lesser than fifty thousand rupees and it might extend up to five lakh rupees, or with both imprisonment and fine. However, this provision provided under the Companies Act, 2013 is rarely used.
In addition, if any information filed by a Director or any other person in the annual return is false by any nature or if he/she failed to mention any fact or material that is true can be punished with imprisonment for a term which is not lesser than six months and which could extend up to 10 years. Further, he/she can also be liable for payment of a fine which is not lesser than the amount subject to the fraud involved and it may extend to an amount three times of the sum concerned with the fraud.
B. Consequences of Default – For Company
The following are some of the penal consequences for a company that has not filed its annual return:
Penalty
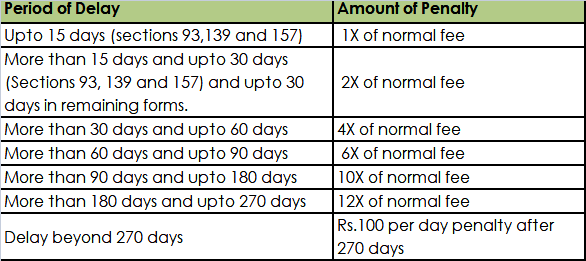
Normally, the Government fee for filing or registering any document under the Companies Act required or authorized to be filed with the Registrar is Rs.200. A private limited company would be required to file form MGT-7 and form AOC-4 each year and the government fee applicable if filed on time would be Rs.400. In case of delay in filing of annual return, the penalty as mentioned would be applicable:
The penalty for not filing a company’s annual return (Form MGT-7 and Form AOC-4) is increased to Rs.100 per day w.e.f.July 1, 2018.
Strike-Off
In case the company has not filed its Annual Return for the last two financial years continuously, then such companies would be termed as an “inactive company”. On such a classification, the bank account of the company could be frozen. Further, the Registrar could also issue a notice to the Company and initiate strike-off of the company from the MCA records.
In case you need any assistance to file annual return for your company, you can contact us at Director@Sunkrish.com