
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) on Tuesday pared its growth forecast for the Indian economy by half a percentage point to 6.7% for 2017, blaming the lingering disruptions caused by demonetisation of high value currencies last year and the roll out of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
However, IMF said the structural reforms undertaken by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government would trigger a recovery—above 8% in the medium term.
In its latest World Economic Outlook, IMF said the global economy is going through a cyclical upswing that began midway through 2016. It raised the global growth estimate marginally for 2017 to 3.6% while flagging downside risks. The upward revisions in its growth forecasts including for the euro area, Japan, China, emerging Europe, and Russia more than offset downward revisions for the United States, the United Kingdom, and India. 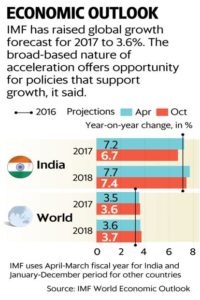
“In India, growth momentum slowed, reflecting the lingering impact of the authorities’ currency exchange initiative as well as uncertainty related to the midyear introduction of the countrywide Goods and Services Tax,” it said in the WEO.
However, IMF expects the Indian economy to recover sharply in 2018 to grow at 7.4%, though 30 basis points lower than its earlier estimate in April.
One basis point is one-hundredth of a percentage point.
In its South Asia Economic Focus (Fall 2017) released on Monday, the World Bank reduced India’s GDP growth forecast to 7% for 2017-18 from 7.2% estimated earlier, blaming disruptions caused by demonetisation and GST implementation, while maintaining at the same time that the Indian economy would claw back to grow at 7.4% by 2019-20.
Both the Asian Development Bank as well as the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) have also cut their growth projections for India to 7% and 6.7%, respectively, for fiscal 2017-18.
IMF said a gradual recovery in India’s growth trajectory is a result of implementation of important structural reforms. GST, “which promises the unification of India’s vast domestic market, is among several key structural reforms under implementation that are expected to help push growth above 8% in the medium term,” it added.
The multilateral lending agency said India needs to focus on simplifying and easing labour market regulations and land acquisition procedures which are long-standing requirements for improving the business climate. It also called for briding the gender gap in accessing social services, finance and education to accelerate growth in developing countries like India.
IMF said given faster-than-expected declines in inflation rates in many larger economies, including India, “the projected level of monetary policy interest rates for the group is somewhat lower than in the April 2017 WEO.”
In its monetary policy review last week, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) kept its policy rates unchanged and marginally raised its inflation forecast for rest of the year.
Highlighting the growing income inequality within and among emerging market economies, IMF said a country’s growth rate does not always foretell matching gains in income for the majority of the population. “In China and India, for example, where real per capita GDP grew by 9.6% and 4.9% a year, respectively, in 1993–2007, the median household income is estimated to have grown less—by 7.3% a year in China and only 1.5% a year in India,” it said.
Source: Live Mint






